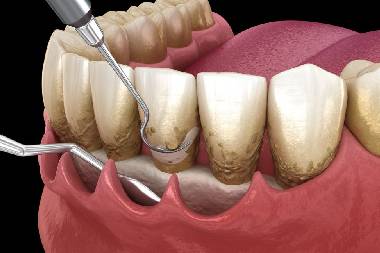
Periodontal Surgery is a specialized dental procedure aimed at treating advanced gum disease (periodontitis) or improving the structure and aesthetics of the gums and supporting bone. It’s typically performed by a periodontist, a dentist with advanced training in managing gum tissues and bone support around teeth and dental implants.
What Is Periodontal Surgery?
Periodontal (gum) surgery is done to:
Remove infection and diseased tissue
Clean deep pockets of bacteria
Regenerate lost bone or soft tissue
Reshape the gums for aesthetic or functional reasons
Prepare for or maintain dental implants
When Is It Needed?
You may need periodontal surgery if you have:
Deep periodontal pockets that don’t improve with scaling/root planing
Gum recession or overgrowth
Loose teeth due to bone loss
Infected or inflamed gums (chronic periodontitis)
Bone defects around teeth or implants
Excessive gum display (“gummy smile”)
Before or during implant placement
Types of Periodontal Surgery
| Procedure | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Flap Surgery (Pocket Reduction Surgery) | Removes bacteria from deep pockets by lifting the gums |
| Gingivectomy | Removes excess or overgrown gum tissue |
| Gingivoplasty | Reshapes healthy gum tissue for aesthetics |
| Crown Lengthening | Exposes more of the tooth by removing gum/bone tissue |
| Bone Grafting | Rebuilds bone lost due to periodontitis |
| Guided Tissue Regeneration (GTR) | Stimulates bone and tissue growth using membranes or proteins |
| Soft Tissue Grafting (Gum Grafts) | Covers exposed roots and restores receding gums |
| Laser-Assisted Periodontal Therapy | Minimally invasive removal of diseased tissue using a dental laser |
What to Expect Before, During, and After Surgery
Before Surgery
Evaluation with X-rays, periodontal charting
Deep cleaning may be done first (scaling & root planing)
Medical history review
Local anesthesia (sometimes sedation)
During Surgery
Incision is made in the gum
Gum is lifted to clean roots and bone
Diseased tissue is removed
Grafting, reshaping, or regeneration is performed if needed
Gums are sutured back in place
After Surgery
Mild swelling, discomfort, and bleeding are normal
Pain managed with medications
Soft diet for a few days
Use antimicrobial mouthwash (e.g., chlorhexidine)
Avoid brushing near the surgical area temporarily
Sutures may be removed after 1–2 weeks